We’ve now started counting the staggering economic cost of the coronavirus shutdown. Two-thirds of Australian businesses have reported taking a hit to their turnover or cash flow, and at least a million Australians could become unemployed. This will no doubt reverberate throughout the housing market.
Before the pandemic, Australia already had about 1.6 million low-income individuals who struggled to meet housing costs. They’re now highly vulnerable to falls in income due to the economic shutdown. The Reserve Bank expects job losses and a lapse in loan repayments to cause a spike in mortgage arrears. Based on its analysis, every percentage point rise in unemployment leads to a 0.8 percentage point increase in the rate of mortgage arrears.
If you’re a mortgage broker with clients affected by this crisis, now is a good time to speak with them and walk them through their options. Perhaps they can negotiate for better interest rates or repayment delays? Or is refinancing their best option? For your small business clients, read about where they can get financial help.
Figure 1: Impacts of COVID-19 on Australian business operations
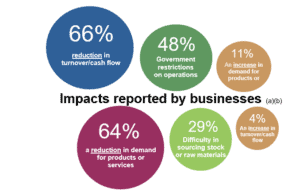
(a) Proportions of businesses currently trading
(b) Businesses could select more than one option
Source: Australian Bureau of Statistics
Note: Data collected during the week starting 30 March 2020.
Sign of a downturn
While it’s still too early to tell the full impact on the housing market, analysts expect housing demand and values to tumble. One sign of this could be a recent jump in housing stock sitting on the market for up to 60 days.
Data from SQM Research shows residential property listings across Australia rose 3.7% in March. Listings that have been on the market for 30 to 60 days surged 74%, suggesting slowing sales activity in March.
According to SQM Managing Director Louis Christopher, residential listings are starting to pile up. “This may reflect the start of a capital city housing market downturn due to the health and economic impact of COVID-19.”
CoreLogic’s data at the end of March suggests a “sudden, sharp slowdown” in housing market activity. Its daily index showed a fall in rolling 28-day growth for that month.
“Although the series remains in positive territory, the trend is clearly pointing towards a slowdown in growth that is likely to move into negative territory over the coming months,” says Eliza Owen, CoreLogic’s Head of Australian Research.
Figure 2: Rolling 28-day change in CoreLogic’s Daily Home Value Index
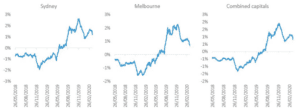
Source: CoreLogic
A sharp rise in unemployment in the coming months could see housing prices plummet as a result of mortgage defaults. AMP Capital Chief Economist Shane Oliver expects prices to drop 20% or more in the worst-case scenario.
“If unemployment overwhelms the system and the economic downturn goes well beyond the period due to the virus … we’re going to see much bigger falls in house prices,” says Oliver.
The high level of household debt is also making the housing situation more precarious. Australia’s household debt to income ratio stands at around 187%.
Figure 3: Ratios of housing prices and household debt to income
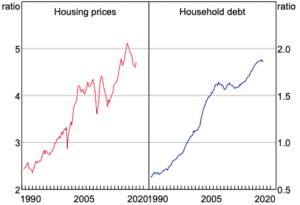
Source: Reserve Bank of Australia
“The current high level of household debt amplifies the risk of unemployment,” says CoreLogic Head of Research Tim Lawless.
Falling buyer queries
The buyer side also gives us a glimpse of where the housing market is heading.
CoreLogic’s survey of mainly property agents in March shows buyer queries have nosedived. About one-third of respondents had seen a fall in buyer enquiries of more than 50%.
“This result is in line with a sharp decline in consumer sentiment and rising unemployment, which would see people less confident or able to purchase property,” says Owen.
If it’s any consolation, the federal government’s $130 billion wage subsidy provides a lifeline to vulnerable mortgagors.
“It’s unlikely that fiscal stimulus will be able to keep Australia out of recession over March/June quarters,” says Oliver. “But it will help protect the economy from collateral damage by minimising business failures and household defaults.”




