After a year many business owners would rather forget, lending to business is picking up.
Data from the Reserve Bank of Australia shows business credit climbed 1.6% in June 2021, the highest monthly growth since March 2020. On an annual basis, business lending went up 0.6% after four straight months of negative growth.
Lending to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) was a significant contributor to this growth. The volume of lending to SMEs resumed growth in the June 2021 quarter, following the trend set by the large business sector, where lending had been on the rise since the start of 2021.
This signals improved confidence among SMEs.
According to a recent report by business lender Banjo, 65% of respondent SMEs intended to seek funding in the next 12 months to help grow their business. The majority (81%) felt confident about the long-term prospects of their business. The survey was conducted in March 2021.
Figure 1: Australian credit growth by sector
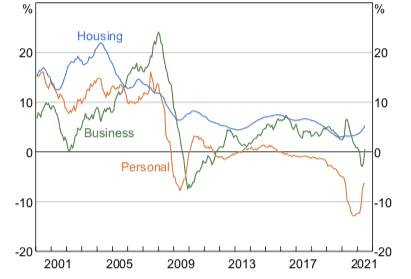
Source: Reserve Bank of Australia Chart Pack, July 2021
This signals improved confidence among SMEs.
According to a recent report by business lender Banjo, 65% of respondent SMEs intended to seek funding in the next 12 months to help grow their business. The majority (81%) felt confident about the long-term prospects of their business. The survey was conducted in March 2021.
Increased confidence supported recent business credit growth, according to BankSA Senior Economist Jarek Kowcza.
“Heading into the lockdowns, elevated confidence and high utilisation of existing productive capacity suggested that businesses were in a good position to increase their levels of investment to create additional capacity,” says Kowcza.
“Business investment is also currently supported by generous tax incentives from the government and continued accommodative monetary policy settings,” he adds.
Declining confidence levels
However, ongoing lockdowns will inevitably cast a pall over business confidence and appetite for credit. And based on Australia’s 2020 experience, banks might think twice about offering loans to businesses from hard-hit industries.
In fact, NAB’s business surveys in June and July showed that business confidence has already taken a hit. Confidence fell nine points to +11 index points in June. And in July, it sharply declined by 19 points to -8 index points.
Figure 2: NAB business survey
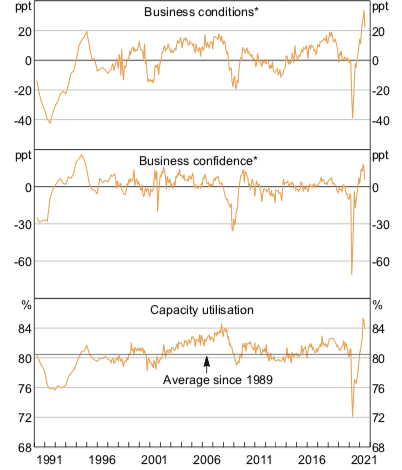
* Net balance; deviation from average since 1989.
Source: Reserve Bank of Australia Chart Pack, July 2021
“Confidence took a big hit in the month, with optimism collapsing on the back of ongoing restrictions,” says NAB Group Chief Economist Alan Oster in the July report.
“New South Wales declined by a very large 27 points on the back of ongoing uncertainty about how quickly the outbreak could be contained,” he adds. “That said, confidence was softer everywhere with uncertainty over the spread of the virus in the other states and border closures.”
Quick recovery to support credit growth
Still, Oster is confident that recovery will be fast.
“We know that once restrictions are removed, the economy has tended to rebound relatively quickly,” he says.
Kowcza agrees. “This [recovery will be] supported by pent-up demand from consumers and support packages from the federal and state governments. Additionally, monetary policy settings remain extremely accommodative and supportive of lending growth.”
Over the long term, Kowcza expects continued economic recovery to buoy credit growth. Significant investment tax incentives from the Australian government will also provide a boost.
“Some businesses have also been running down the large cashflow buffers they accumulated during the pandemic, which increases the likelihood they will require additional credit,” he says.
“These factors will continue to support demand for business credit into the future.”




