With home prices predicted to dive by as much as 32%, will a pandemic-induced property slump finally make housing affordable? Could it be a panacea for Australia’s housing affordability problem, where soaring prices benefited mostly high-income homeowners and locked others out of the market or saddled them with huge debts?
While falling prices could help some would-be buyers get a foot in the door, rising unemployment and job uncertainty mean not all of them can or will take advantage of this trend. For those who recently bought their first home, a housing bust could leave them with negative equity.
According to researchers from the University of Melbourne and Swinburne University of Technology, those who bought their homes at the peak of the housing boom (between FY2014–15 and FY2017–18) and have recently lost their jobs are facing the biggest risk.
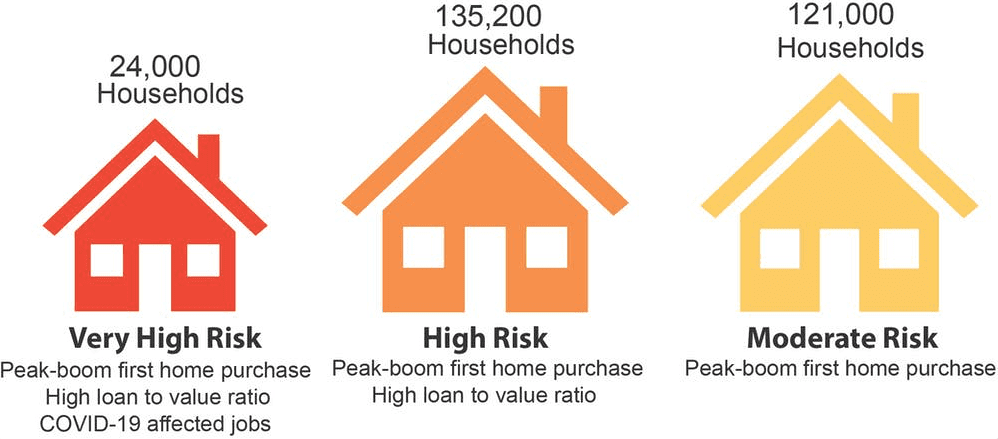
“We estimate 24,000 households are at very high risk because they took out large loans that might soon exceed their home value and also work in sectors with high job losses,” say Ilan Wiesel from the University of Melbourne and Liss Ralston and Wendy Stone from Swinburne University of Technology in this article. “Another 135,200 are at high risk and 121,000 are at moderate risk.”
In relation to the 24,000 households, members borrowed more than 80% of the value of their property and work in industries severely hit by the pandemic. Similarly, 135,200 buyers with high loan-to-valuation ratios are at risk of having homes worth less than their debt.
Figure 1: Recent homebuyers at risk of a pandemic-induced housing bust
Debt burden
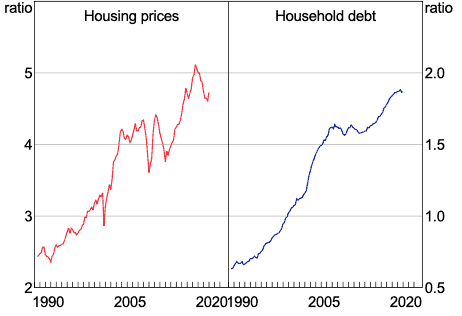
Australia’s house price boom means that recent buyers took out larger loans to acquire properties. According to the Australian Finance Group’s latest mortgage index, the national average size of a broker-originated mortgage rose to more than $543,000 in the March 2020 quarter, up from $504,000 the previous year and by 22% from five years ago.
Figure 2: Ratio of home prices and household debt to household disposable income*
A surge in unemployment is likely to increase the number of people who fall behind on mortgage repayments and could force many to sell.
AMP Capital Chief Economist Shane Oliver expects unemployment to be around 8% once government stimulus programs such as the JobKeeper Payment scheme end. “This, in turn, is likely to lead to some increase in mortgage defaults as bank payment holidays for around 440,000 mortgages end, boosting forced sales and acting as a drag on property demand,” he says.
Temporary relief
Some good news is that would-be buyers can take advantage of the lower rents being offered around the country to accelerate savings towards a home loan deposit. However, this window may not be open for long, according to Wiesel, Ralston and Stone.
“The sudden decline in international students and short-term rentals has increased long-term rental vacancies in some areas. Reports suggest rents are going down, especially at the upper end of some rental markets,” they say.
“However, in the longer run, the slowdown in housing construction will create supply shortages, leaving rental vacancies low and rents high. Many landlords, mostly ‘mum and dad’ investors, have taken large loans to finance their property investment. They will need to keep rents high to hold on to their investment properties.”




